Around 5-10% of newborns need assistance to start breathing at birth. For years, doctors and nurses have relied on manual methods to record the exact time a baby is born, often to the minute. But when it comes to newborn resuscitation, timing matters — especially during the crucial “golden minute,” when every second counts. Enter AI-powered thermal cameras, an innovative solution that promises to revolutionize the way we care for newborns by detecting the time of birth (ToB) with incredible accuracy.
By combining artificial intelligence (AI) with thermal imaging technology, researchers aim to eliminate human error in birth time recording and provide precise data to improve neonatal care. This game-changing approach offers immense potential, but the journey to get there involves overcoming some serious technical challenges.
Why Accurate Time of Birth is So Critical
In neonatal care, precision isn’t just about being fancy. It’s about saving lives. The first 60 seconds after birth, known as the "golden minute," is a window in which quick intervention can drastically reduce the risk of long-term damage or even death from birth asphyxia. The current method for logging a baby's birth time is often manual and prone to error. Nurses or doctors, distracted by the delivery, may record the time off by several seconds—or even a minute. And while a minute may not seem like much, in neonatal care, those extra seconds can mean the difference between life and death.
Think of it like trying to stop a stopwatch at the exact moment something happens. Your reaction time is always a little off, right? In a fast-paced delivery room, it’s even harder. This is why AI can step in to handle the precision work humans struggle with.
The Power of AI in Neonatal Care
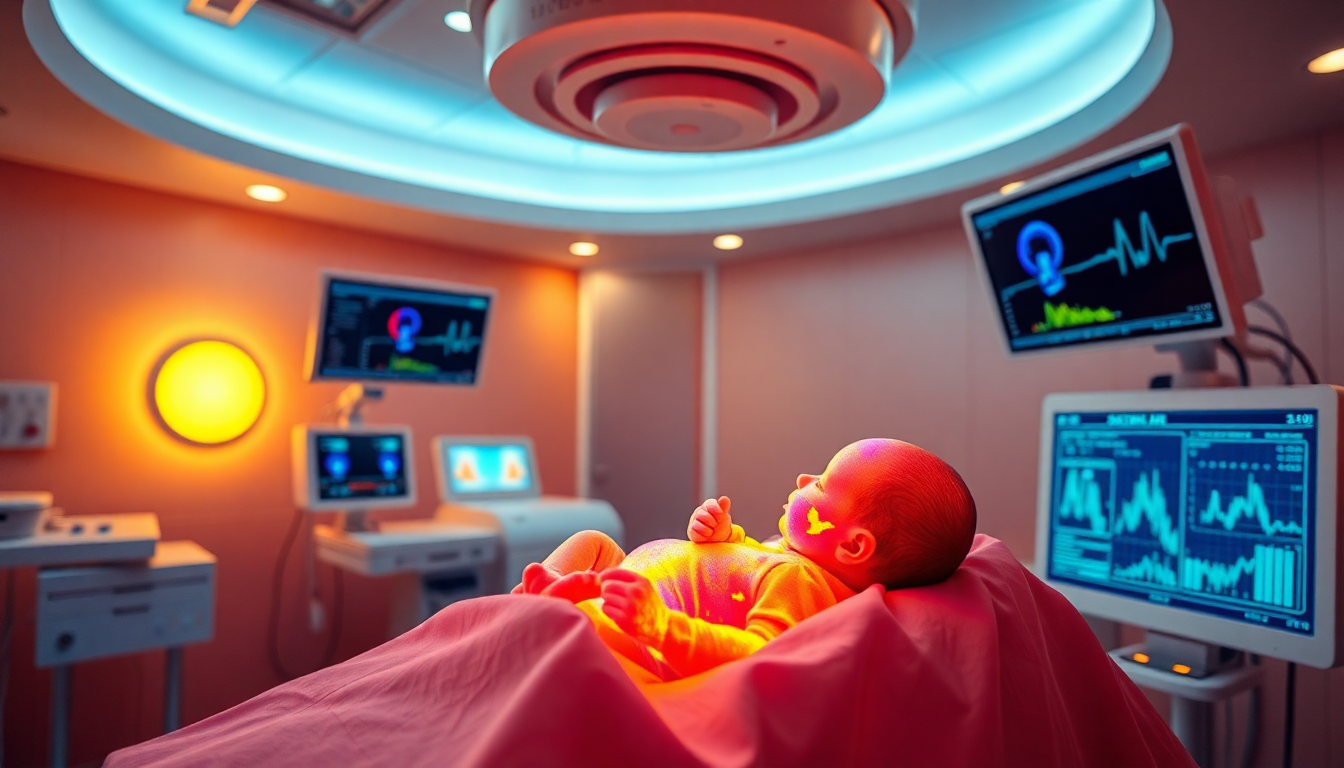
AI’s role in medicine is growing, from diagnosing diseases to helping doctors make more informed decisions. But in neonatology, the idea of using AI to pinpoint the exact moment a baby is born is new and exciting. The AI system for detecting birth time uses thermal cameras that can capture heat signatures—basically, how warm a body is compared to its surroundings. AI can distinguish between different heat patterns, identify the newborn, and calculate the exact second they enter the world.
The technology draws upon deep learning models, a type of AI that’s particularly adept at recognizing patterns. Deep learning works by feeding an AI system massive amounts of data—in this case, thermal images of newborns—and training it to recognize specific patterns that signal birth. This could be a game-changer for neonatal care, much like AI’s influence in cancer research and drug discovery.
Thermal Imaging: Seeing What Our Eyes Can't
Thermal imaging cameras detect the heat emitted by an object—in this case, the newborn baby. The AI-driven system tracks the baby’s body temperature relative to everyone else in the room. This ensures that the detection process remains non-invasive, meaning no one has to attach anything to the baby or disturb the mother.
This is particularly important in a delivery room, where privacy and minimal interference are paramount. AI can scan the room without getting in anyone's way, detecting the newborn's presence even before they’re handed off to a nurse or placed in an incubator.
Think of thermal imaging like the night vision goggles used by the military. While the human eye can’t see in the dark, these goggles can pick up on heat signatures, making things visible that are otherwise hidden. Similarly, thermal cameras can detect heat differences and recognize when the baby is fully born.
Overcoming the Challenges: Adaptive Normalization
Using thermal cameras may sound simple, but it’s not without its challenges. Hospitals are dynamic environments with fluctuating room temperatures and varying body heat from everyone present. These inconsistencies can make it hard for AI to detect the newborn accurately. That’s where adaptive normalization comes into play.
Adaptive normalization essentially means calibrating the system to account for variations in the data, like a human adjusting to new light conditions when walking from a dark room into bright sunlight. Researchers used a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) to help the system focus only on the important temperature variations, such as the baby’s body heat, while ignoring other distracting elements, like medical equipment or warm blankets.
You can think of GMM as the system’s way of filtering out "noise"—anything that could throw off the AI’s ability to recognize the birth moment. It’s like tuning out background chatter in a busy café to focus on what your friend is saying. Adaptive normalization ensures the AI only pays attention to what matters: the newborn.
AI Accuracy: Better Than Human Judgment
In a study conducted by researchers at the University of Stavanger and Laerdal Medical, the AI-driven ToB detection achieved a precision of 88.1% and a recall of 89.3%. In plain English, this means the AI system was able to accurately detect the birth with a high level of success.
Moreover, the system's median deviation from manually recorded birth times was just 2.7 seconds. This is a massive improvement over human records, where it’s easy to be off by an entire minute or more. In a delivery room where time is of the essence, those seconds could be vital.
It’s comparable to how we now trust GPS over our own sense of direction when driving. Sure, you could figure out your route without it, but the GPS gets you there more reliably—and in a pinch, like when you’re late for a meeting, you’ll definitely want that level of precision.
Privacy and Ethical Considerations
Using AI in hospitals can raise eyebrows, especially when it comes to privacy. But in this case, thermal cameras offer a significant advantage: they capture heat, not detailed visual images. This means healthcare providers and mothers don’t have to worry about being recorded in compromising positions.
Still, the deployment of any new technology in healthcare must go through rigorous ethical review. The team behind this AI system worked with ethical committees to ensure that the data collected would be used responsibly and that the privacy of patients and staff would be protected. In fact, the system has already been approved by REK-Vest, Norway’s Regional Ethical Committee.
It’s a lot like the security cameras used in smart homes. They record motion but can be set to avoid capturing detailed personal information. AI-driven thermal cameras follow a similar principle, focusing on the thermal signatures of newborns without invading anyone’s privacy.
Applications Beyond Birth Detection
AI and thermal imaging aren’t just limited to recording time of birth. The technology can also be used for other neonatal care processes. For example, thermal imaging can track a baby’s respiratory rate or detect potential complications like hypoxia (low oxygen levels). This makes it a versatile tool for keeping an eye on the newborn’s health without unnecessary physical intervention.
In the future, we could see AI systems integrated into smart incubators, constantly monitoring the baby’s vital signs in real-time. This would be similar to how wearable health tech, like Fitbit or Apple Watch, tracks heart rate and physical activity 24/7.
The Future of Neonatal Care
This AI-driven birth detection is part of a larger trend in healthcare toward automation and smart systems. The integration of AI in neonatal care could open doors to other innovations, from AI-driven debriefings for doctors after a difficult birth to smart algorithms that can predict complications before they happen.
Just as AI is changing fields like autonomous driving and logistics, its impact on neonatal care could redefine how we approach critical moments in the birthing process. Imagine a world where doctors have access to real-time, second-by-second data that helps them make quicker, more informed decisions during a newborn's first moments. This isn’t just a far-off dream—it's the future of healthcare, and AI is making it possible.
What Does This Mean for You?
At the end of the day, AI and thermal cameras aren’t just about making medical records more precise—they’re about saving lives and improving outcomes for some of the most vulnerable patients. This technology reduces human error, gives healthcare professionals better tools to do their jobs, and ultimately helps babies get the care they need right when they need it.
For parents, the peace of mind that comes with knowing their baby’s first moments are being monitored with the utmost precision is priceless. It’s akin to the security we feel knowing there’s a backup plan in place for emergencies, like having a fire extinguisher in the kitchen.
The development of AI-driven birth detection may be one small step for hospitals but one giant leap for neonatal care. As these systems continue to evolve, we’re likely to see even more groundbreaking innovations in how we care for our littlest patients.
What Do You Think?
What do you think about AI being used in such a critical way in hospitals? How do you feel about machines taking on these important roles? Would you feel more secure knowing your baby’s first moments are being captured with AI-driven precision? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
And while you’re here, consider becoming a part of the iNthacity community. Apply to become permanent residents and citizens of the “Shining City on the Web”. Don’t forget to like, share, and participate in the debate!
It's not over...check out our gripping short story that continues the conversation: The Silent Symphony: A Futuristic Tale of AI, Obstetrics, and Human Care


















Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.